BITMAP Image Format
The BMP image file also called DIB image file. DIB means (Device Independent Bitmap). It is an image file used to store image data with different bit levels. This article describes the BITMAP file formats used in Microsoft windows, and IBM os/2 machines in byte by byte level. Its file extension is either BMP or DIB. The sample 24 bit BMP and DIP image are shown below.
Contents :
- DIM or BMP Image file format
- Bitmap File Header
- Bitmap Information
- Bitmap Information Field details
- Color Palette
- Color Palette Field details
- Bitmap Data
- Bitmap Data Field details
A typical BMP has the following structure. It consist if BMP File Header, Bitmap Information, Color palette and Bitmap Data.
| BMP File Header | BMP file general information. |
| Bitmap Information (DIB header) | Detailed information about the BMP image. |
| Color Palette | Color definitions used for indexed color bitmaps. |
| Bitmap Data | pixel by pixel image data |
Bitmap File Header:
For any file types first few bytes are identify of that files. It identifies the file types. Like that here also first two bytes are the identity bytes. Generally first two bytes has the value of 'BM'. All the values are stores in little-endian encoding format. Generally the first 14 bytes contains the BMP file header information.
| Offset | Size | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 0000h | 2 bytes |
|
| 0002h | 4 bytes | BMP file size in bytes |
| 0006h | 2 bytes | reserved |
| 0008h | 2 bytes | reserved |
| 000Ah | 4 bytes | the offset, i.e. starting address, of the byte where the bitmap data can be found. |
Bitmap File Header Field details:
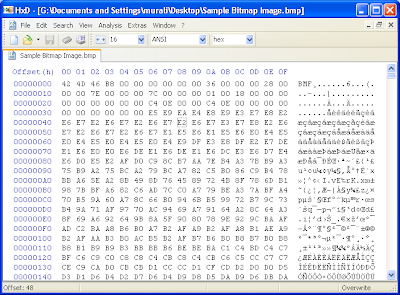
From the sample image. The first two bytes are the identity bytes so it's 'B' and 'M'.
File Size:
The Image size is 47174 bytes (refer size.png). 47174 equvalent of hex value is B846. The image representation is little-endian so the value becomes 05 th byte = 00, 04 th byte = 00, 03rd byte = B8, 02 nd byte = 46.
Offset : Starting address of bitmap data. I.e the starting address of the bitmap data. In the sample image it is 36 (Represented in byte 0Ah) because it does have any extra color palate data or header information so it would be 36.
Bitmap Information (DIB header):
The header bytes show the detailed information of BMP image. Here I am giving five versions of header two from IBM OS 2 versions and three from Microsoft versions. Because Microsoft extended the DIB format several times. So that the new header format is used instead of the older ones for providing more functionality. Since windows GDI loads the bitmap file into the system.
| Size | Header | Identified by | Supported by the GDI of |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | OS/2 V1 | BITMAPCOREHEADER | OS/2 and Windows 3.0 and above |
| 64 | OS/2 V2 | BITMAPCOREHEADER2 | |
| 40 | Windows V3 | BITMAPINFOHEADER | Windows 3.0 and above |
| 108 | Windows V4 | BITMAPV4HEADER | Windows 95/NT4 and above |
| 124 | Windows V5 | BITMAPV5HEADER | Windows 98/2000 and above |
The table has all the five formats of header information’s. From the size of the header system identifies which version of header is used. The header size is in offset 0Eh.
BITMAPCOREHEADER or OS/2 V1 Header Structure
This structure is used in all OS/2 and also all Windows versions since Windows 3.0. This is a simple structure its size is 12 bytes. It has size, width, height, planes and bitcount. The offset and byte values are shown in the following table. This is also called as OS/2 V1 bitmaps. This format does not use any compression algorithms and it does not have 16 or 32 bit depths. The values in the header are unsigned integers. 32 bit version with alpha channel is introduced in Windows XP and it is used for its login screen. It is supported by Adobe Photoshop version 7 and above, Adobe flash and GIMP
| Offset | Size | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Eh | 4 | size of the header (12 bytes) |
| 12h | 2 | bitmap width in pixels. |
| 14h | 2 | bitmap height in pixels. |
| 16h | 2 | the number of color planes; 1 is the only legal value |
| 18h | 2 | the number of bits per pixel. Typical values are 1, 4, 8 and 24. |
typedef struct tagBITMAPCOREHEADER {
DWORD bcSize;
WORD bcWidth;
WORD bcHeight;
WORD bcPlanes;
WORD bcBitCount;
} BITMAPCOREHEADER, *PBITMAPCOREHEADER;
BITMAPCOREHEADER2 or OS/2 V2 Header Structure
This version has few additional fields over BITMAPINFOHEADER. The BITMAPINFOHEADER header info is given below. This is also called OS/2 V2 header used in IBM OS/2 Versions. Its header size would be 64 bytes. The typical C structure is given below.
typedef struct {
DWORD bc2Size;
DWORD bc2Width;
DWORD bc2Height;
WORD bc2Planes;
WORD bc2BitCount;
DWORD bc2Compression;
DWORD bc2SizeImage;
DWORD bc2XRes;
DWORD bc2YRes;
DWORD bc2ClrUsed;
DWORD bc2ClrImportant;
/* same as BITMAPINFOHEADER until this point */
WORD bc2ResUnit;
WORD bc2Reserved;
WORD bc2Orientation;
WORD bc2Halftoning;
DWORD bc2HalftoneSize1;
DWORD bc2HalftoneSize2;
DWORD bc2ColorSpace;
DWORD bc2AppData;
} BITMAPCOREHEADER2;
BITMAPINFOHEADER Header Structure:
All Windows versions since Windows 3.0 uses this header format. Its size is 40 bytes. For compatibility reason almost all versions of OS uses this header format. It has all the information generally used. All values are unsigned integers.
| Offset # | Size | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 0Eh | 4 | size of the header (40 bytes) |
| 12h | 4 | bitmap width in pixels (signed integer). |
| 16h | 4 | bitmap height in pixels (signed integer). |
| 1Ah | 2 | number of color planes being used. Must be set to 1. |
| 1Ch | 2 | the number of bits per pixel, I.e color depth of the image. Values are 1, 4, 8, 16, 24 and 32. |
| 1Eh | 4 | compression method being used. |
| 22h | 4 | image size. This is the size of the raw bitmap data (0 for BI_RGB bitmaps), and should not be confused with the file size. |
| 26h | 4 | horizontal resolution of the image. (pixel per meter, signed integer) |
| 2Ah | 4 | vertical resolution of the image. (pixel per meter, signed integer) |
| 2Eh | 4 | number of colors in the color palette, or 0 to default to 2n. |
| 32h | 4 | number of important colors used, or 0 when every color is important; generally ignored. |
typedef struct {
uint32_t header_sz;
int32_t width;
int32_t height;
uint16_t nplanes;
uint16_t bitspp;
uint32_t compress_type;
uint32_t bmp_bytesz;
int32_t hres;
int32_t vres;
uint32_t ncolors;
uint32_t nimpcolors;
} bmp_dib_v3_header_t;
Bitmap Compression Methods.
The following compression methods are used in BMP Image which are shown in the following table.
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| BI_RGB | An uncompressed format. |
| BI_RLE8 | RLE compression format for bitmaps with 8 bpp. The compression format is a two-byte format consisting of a count byte followed by a byte containing a color index. If bV5Compression is BI_RGB and the bV5BitCountmember is 16, 24, or 32, the bitmap array specifies the actual intensities of blue, green, and red rather than using color table indexes. |
| BI_RLE4 | RLE compression format for bitmaps with 4 bpp. The compression format is a two-byte format consisting of a count byte followed by two word-length color indexes. |
| BI_BITFIELDS | Specifies that the bitmap is not compressed and that the color table consists of three DWORD color masks that specify the red, green, and blue components of each pixel. Valid when used with 16- and 32-bpp bitmaps. |
| BI_JPEG | JPEG Compression is used. It can achieve a compression ratio of 20:1 with little noticeable loss. |
| BI_PNG | PNG file Interchange Format compression. |
typedef enum {
BI_RGB = 0,
BI_RLE8,
BI_RLE4,
BI_BITFIELDS,
BI_JPEG,
BI_PNG,
} bmp_compression_method_t;
BITMAPV4HEADER Structure:
The BITMAPV4HEADER structure is an extended version of the BITMAPINFOHEADER structure. This header size is 108 bytes. It is supported by Windows 95/NT4 and above. The C structure for this header is
typedef struct {
DWORD bV4Size;
LONG bV4Width;
LONG bV4Height;
WORD bV4Planes;
WORD bV4BitCount;
DWORD bV4V4Compression;
DWORD bV4SizeImage;
LONG bV4XPelsPerMeter;
LONG bV4YPelsPerMeter;
DWORD bV4ClrUsed;
DWORD bV4ClrImportant;
DWORD bV4RedMask;
DWORD bV4GreenMask;
DWORD bV4BlueMask;
DWORD bV4AlphaMask;
DWORD bV4CSType;
CIEXYZTRIPLE bV4Endpoints;
DWORD bV4GammaRed;
DWORD bV4GammaGreen;
DWORD bV4GammaBlue;
} BITMAPV4HEADER, *PBITMAPV4HEADER;
refer : http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd183380(VS.85).aspx for more about BITMAPV4HEADER Structure.
BITMAPV5HEADER Structure:
The BITMAPV4HEADER structure is also an extended version of the BITMAPINFOHEADER structure. This header size is 124 bytes. It is supported by Windows 98/2000 and above. The C structure for this header is
typedef struct {
DWORD bV5Size;
LONG bV5Width;
LONG bV5Height;
WORD bV5Planes;
WORD bV5BitCount;
DWORD bV5Compression;
DWORD bV5SizeImage;
LONG bV5XPelsPerMeter;
LONG bV5YPelsPerMeter;
DWORD bV5ClrUsed;
DWORD bV5ClrImportant;
DWORD bV5RedMask;
DWORD bV5GreenMask;
DWORD bV5BlueMask;
DWORD bV5AlphaMask;
DWORD bV5CSType;
CIEXYZTRIPLE bV5Endpoints;
DWORD bV5GammaRed;
DWORD bV5GammaGreen;
DWORD bV5GammaBlue;
DWORD bV5Intent;
DWORD bV5ProfileData;
DWORD bV5ProfileSize;
DWORD bV5Reserved;
} BITMAPV5HEADER, *PBITMAPV5HEADER;
refer : http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd183381(VS.85).aspx for more about BITMAPV5HEADER Structure.











0 comments:
Post a Comment